The working principle of semiconductor thermistors can be divided into two categories according to the temperature characteristics of thermal resistance. With the increase of temperature resistance, thermal resistance with positive temperature coefficient, and conversely, resistance of thermal resistance with negative temperature coefficient.
The working principle of positive temperature coefficient thermistor:
This thermal resistance is based on barium titanate (BaTio3) as the basic material, and then mixed with an appropriate amount of rare earth elements. Pure barium titanate is an insulating material, but by adding appropriate amounts of rare earth elements (such as lanthanum (La) and niobium (Nb)), it has become a semiconductor material. It is a polycrystalline material with a crystal grain interface between the crystal grains. For conducting electrons, the crystal grain interface is equivalent to a base. When the temperature is low, due to the electric field of the semiconductor barium titanate, electron conduction easily crosses the barrier, so the resistance value is small; when the temperature rises to the Curie point temperature (ie the critical temperature, that is, the Curie temperature of the component), the electric field will change Be destroyed. Barium titanate (120°C) at the temperature control point cannot help electron conduction through the barrier, so as the resistance value increases, the performance is significantly improved. Because the element does not reach the Curie point, the resistance changes very slowly with temperature. It has constant temperature, automatic temperature and temperature control functions, only fever, redness, no open flame, not easy to burn, AC voltage, DC 3 to 440V can be used, service life Long, suitable for detecting overheating of motors and other electrical equipment.
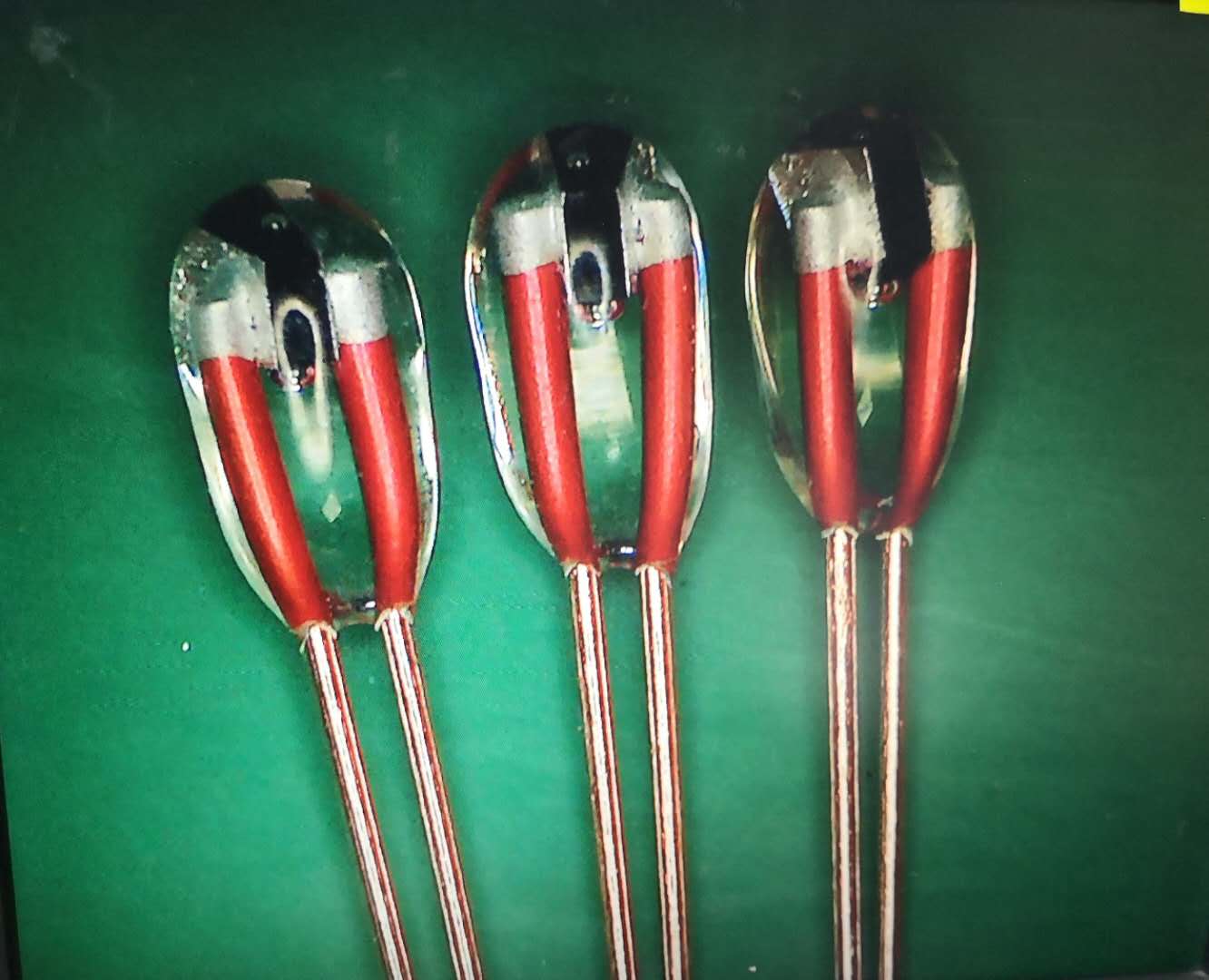

The working principle of NTC thermistor:
Negative temperature coefficient thermal resistance is the main raw material of manganese oxide, cobalt oxide, nickel oxide, copper oxide and aluminum oxide, and is made by ceramic technology. These metal oxide materials have semiconductor properties, which are completely similar to germanium and silicon crystals. The number of carriers (electrons and holes) is smaller and high resistance. As the temperature rises, the number of carriers in the body increases, and the natural resistance value decreases. . There are many types of NTC thermistors, which are used to distinguish low temperature (-60 to 300°C), temperature (300 to 600°C), and high temperature (> 600°C). They have high sensitivity, good stability, fast response speed and long life. The advantage of low price,
Thermal resistance and simple amplifying circuit can detect temperature changes of thousands of degrees, so the thermometer composed of electronic instruments can complete high-precision temperature measurement. The operating temperature of general NTC thermistors is -55 degrees to +315 degrees Celsius, and the operating temperature of special low-temperature thermal resistance is lower than -55, and the highest is -273.
Three main parameters of NTC thermistor:
The working conditions of various thermistors must be within the allowable range of the factory parameters. There are more than ten main parameters of the thermistor: rated resistance value at ambient temperature (maximum operating temperature), power measurement, rated power, rated voltage (maximum operating voltage, current, temperature coefficient, material constant, time constant, etc.). The nominal resistance value is the resistance value at 25 C zero power. In fact, there is a certain error, which should be within +10%.