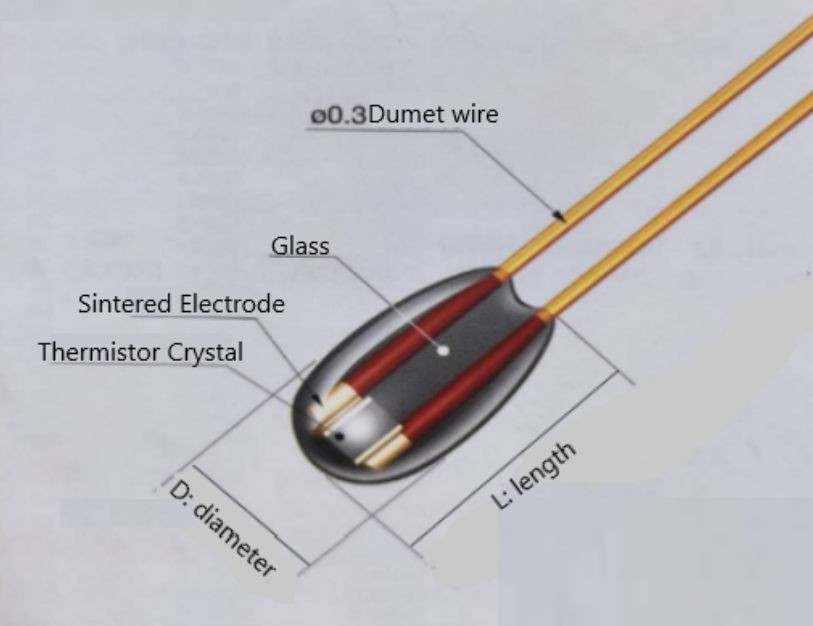
In the world of automotive electronics, precision and reliability are paramount. The performance of critical systems like engine management and climate control can hinge on the effectiveness of temperature sensors. Therefore, glass NTC thermistors play a crucial role in ensuring these systems operate efficiently. This article explores how glass NTC thermistors enhance automotive performance, providing insights into their benefits and applications and why they are the preferred choice for manufacturers.
Understanding Glass NTC Thermistors
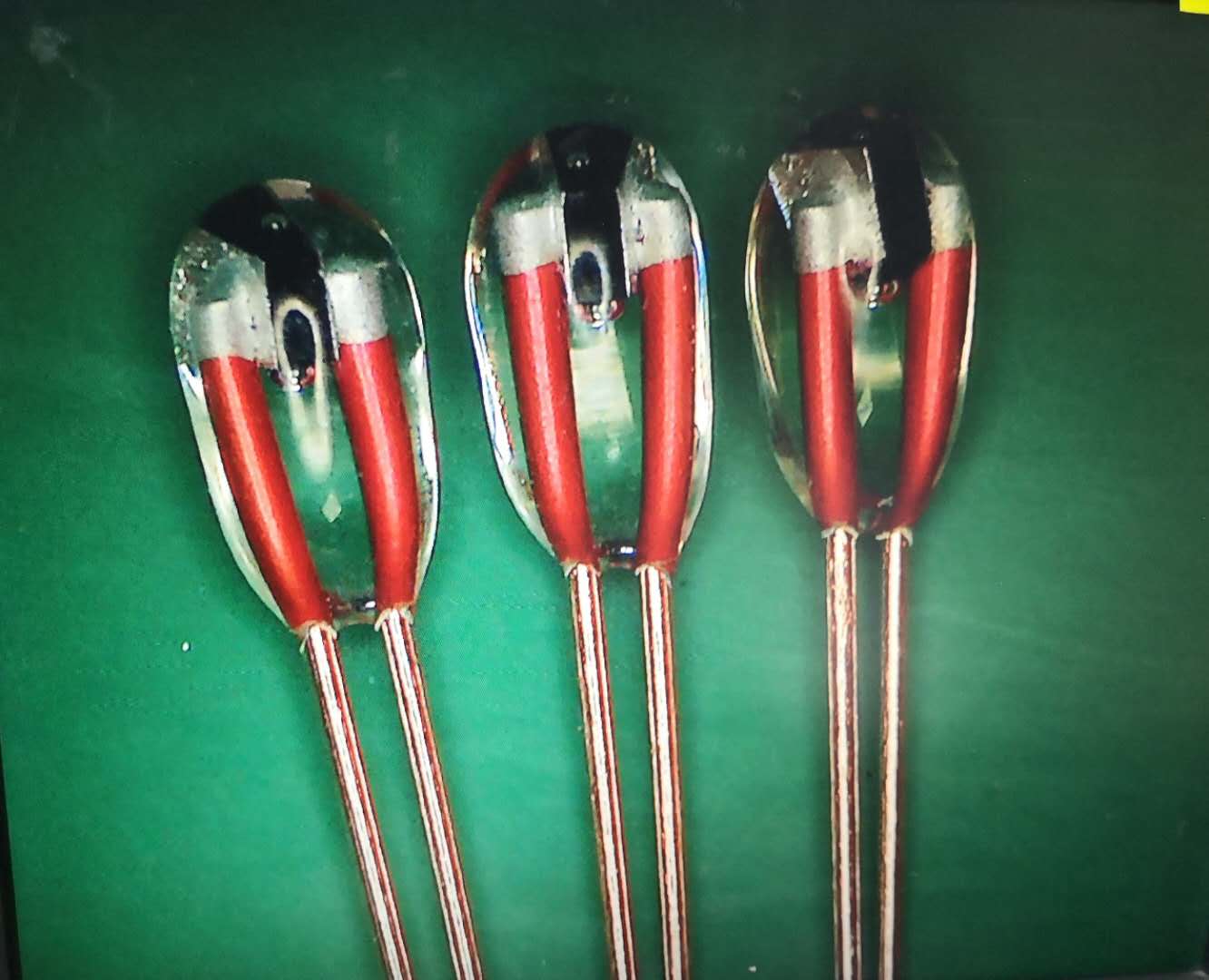
Glass NTC thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors made from a ceramic material encased in glass. Their negative temperature coefficient (NTC) means that as the temperature increases, their resistance decreases. This property makes them ideal for precise temperature measurements across various applications, particularly in the automotive sector.
Key Benefits of Glass NTC Thermistors in Automotive Applications
High Sensitivity
Glass NTC thermistors offer exceptional sensitivity to temperature changes, allowing for accurate readings even in fluctuating conditions. This capability is vital for systems such as engine control units (ECUs) that require precise temperature data to optimize performance.
Wide Temperature Range
These thermistors can operate effectively over a broad range of temperatures, making them suitable for diverse automotive environments—from freezing cold to scorching heat.
Durability
The glass casing provides excellent protection against moisture and contaminants, ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh automotive conditions.
Fast Response Time
The design of glass NTC thermistors allows for rapid thermal response, which is crucial for real-time monitoring and adjustments in automotive systems.
Applications in Automotive Electronics
Engine Management Systems: They monitor engine temperature to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating.
Climate Control Systems: These sensors help regulate cabin temperature by providing accurate readings to the HVAC system.
Battery Management Systems: In electric vehicles, glass NTC thermistors monitor battery temperatures to enhance safety and efficiency.
Exhaust Gas Temperature Monitoring: Proper monitoring of exhaust gas temperatures is essential for maintaining emission standards and ensuring catalytic converter efficiency.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS): Some advanced TPMS utilize glass NTC thermistors to measure tire temperatures, providing critical data that can prevent blowouts and improve fuel efficiency.
Enhancing Performance with Glass NTC Thermistors
The integration of glass NTC thermistors into automotive electronics not only improves performance but also enhances safety. For instance:
- By providing real-time data to the ECU, these sensors enable more efficient fuel usage and reduced emissions.
- In climate control systems, accurate temperature readings ensure passenger comfort while optimizing energy consumption.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications
Electric Vehicle Efficiency:A leading electric vehicle manufacturer integrated glass NTC thermistors into their battery management system. This allowed for precise monitoring of battery temperatures during charging cycles, significantly improving battery life and reducing risk during rapid charging scenarios.
Enhanced Engine Performance: An automotive company utilized glass NTC thermistors in their engine management systems. By accurately measuring coolant temperatures, they were able to optimize fuel injection timing, resulting in improved engine efficiency and reduced emissions.
Future Trends in Glass NTC Thermistor Technology
As the automotive industry continues to evolve toward electrification and automation, the demand for precise temperature sensing solutions will grow. Future trends may include:
- Miniaturization: As vehicles become more compact and sophisticated, smaller glass NTC thermistors will be developed to fit into tighter spaces without compromising performance.
- Smart Sensors: Integration with IoT technology could enable real-time data transmission from glass NTC thermistors to cloud-based systems for enhanced monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Advanced Materials: Research into new materials could lead to even more durable and efficient glass NTC thermistors capable of operating under extreme conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, glass NTC thermistors are indispensable components in modern automotive electronics. Their high sensitivity, durability, and fast response times make them ideal for various applications that demand precision and reliability. By understanding their benefits and applications, manufacturers can leverage these sensors to enhance vehicle performance and safety significantly.